Indication
GHRP-6 (Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-6) is a synthetic hexapeptide classified as a growth hormone secretagogue, primarily indicated in research and clinical contexts involving stimulation of endogenous growth hormone (GH) release. Unlike exogenous growth hormone administration, GHRP-6 promotes physiological GH secretion by activating central regulatory pathways, thereby preserving endocrine feedback mechanisms.
GHRP-6 is commonly indicated in protocols targeting impaired recovery, reduced anabolic signaling, diminished appetite, and age-related decline in GH pulsatility. Additionally, it has been explored in contexts involving sarcopenia, delayed tissue repair, metabolic inefficiency, and recovery deficits associated with intensive physical stress.
Due to its unique appetite-stimulating properties, GHRP-6 is also studied in conditions where inadequate caloric intake or reduced hunger limits anabolic or recovery outcomes.
Contra-Indications
GHRP-6 is contraindicated in individuals with:
- Active malignancies, particularly GH- or IGF-1-sensitive tumors
- Known pituitary adenomas or hypothalamic disorders
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus or severe insulin resistance
- Hypersensitivity to peptide-based compounds
Use during pregnancy and lactation is contraindicated due to insufficient safety data. Individuals with severe cardiovascular disease or endocrine instability should avoid GHRP-6 unless under strict medical supervision.
Administration
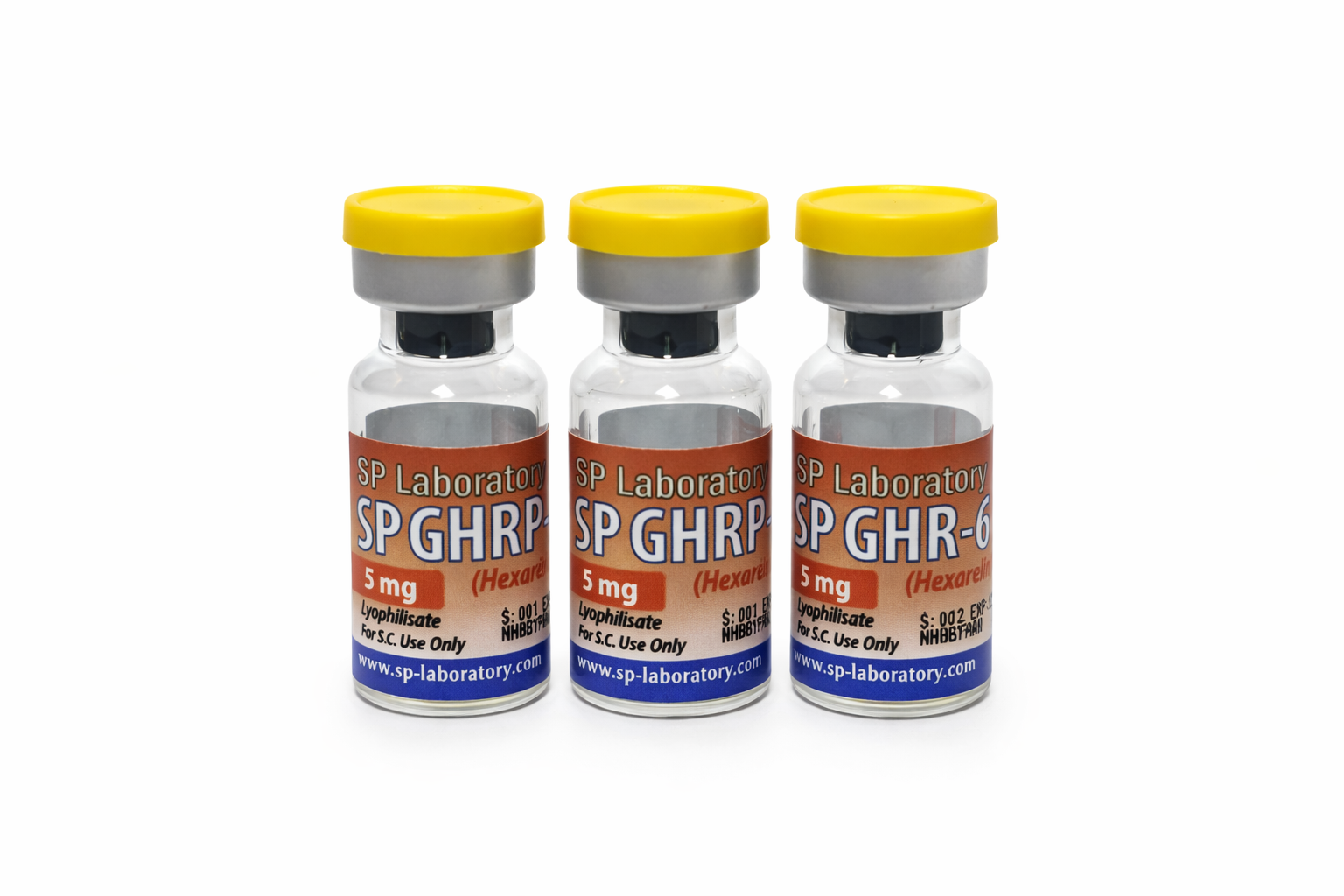
SP GHRP-6 5 mg is supplied as a lyophilized powder requiring reconstitution with bacteriostatic water prior to use. After reconstitution, the solution should be clear and free of particulate matter.
Administration is typically subcutaneous, allowing rapid systemic absorption and effective stimulation of pituitary GH release. Protocols often involve multiple daily administrations to mimic physiological GH pulsatility, particularly when the goal is to enhance recovery or anabolic signaling.
Timing relative to meals is critical, as elevated insulin and glucose levels can blunt GH release. Therefore, administration is commonly scheduled during fasted states or before sleep.
Medical Action
GHRP-6 exerts its primary effect by binding to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R), also known as the ghrelin receptor. Activation of this receptor stimulates the hypothalamic–pituitary axis, leading to pulsatile secretion of growth hormone from the anterior pituitary.
In addition to GH release, GHRP-6 significantly influences hypothalamic appetite centers, resulting in increased hunger signals. This dual action distinguishes it from GHRH analogues and makes it particularly relevant in protocols where caloric intake limits recovery or growth.
Through GH stimulation, GHRP-6 indirectly increases hepatic production of IGF-1, which contributes to protein synthesis, tissue repair, lipid metabolism, and cellular regeneration. Importantly, because GHRP-6 relies on endogenous hormone release, it preserves natural circadian rhythms and feedback inhibition.
Precautions
Careful monitoring of metabolic parameters is advised, particularly in individuals with glucose sensitivity. Appetite increases should be managed through structured nutritional planning to prevent excessive caloric surplus.
Long-term continuous use is not recommended; cycling protocols help preserve receptor sensitivity and endocrine balance. Proper sterile technique during reconstitution and administration is essential to prevent contamination.
Side Effects
Reported side effects are generally dose-dependent and reversible. These may include:
- Increased appetite and food cravings
- Mild water retention
- Temporary lethargy or fatigue
- Injection-site irritation
Excessive dosing may lead to diminished GH response due to receptor desensitization.
Conclusion
SP GHRP-6 5 mg is a well-characterized growth hormone secretagogue with established relevance in recovery, appetite modulation, and anabolic support protocols. By stimulating endogenous GH release while preserving physiological control mechanisms, GHRP-6 offers a structured and adaptable approach to enhancing regenerative signaling.
When applied responsibly, it remains a valuable tool in research-based endocrine modulation strategies.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.